Title and Author of Paper
System R: Relational Approach to Database Management. M. M. Astrahan et al.
Summary
It’s hard to overstate the influence that the System R project had on database design and implementation. After reading this paper it is clear that traditional database architecture has not significantly changed since the System R project. System R provided the first implementation of SQL, the first demonstration of performant transactions, and provided the foundational groundwork in concurrency control and query optimization.
What are the motivations for this work?
The motivation behind System-R was to prove that a relational database was possible — that it could provide adequate performance and query support for Codd’s theoretical relational data model.
What is the proposed solution?
System-R’s architecture is divided in two main components: the relational data system (RDS), and the relational storage system (RSS). Each of these systems has their own interface: the relational data interface (RDI), and the relational storage interface (RSI), respectively.
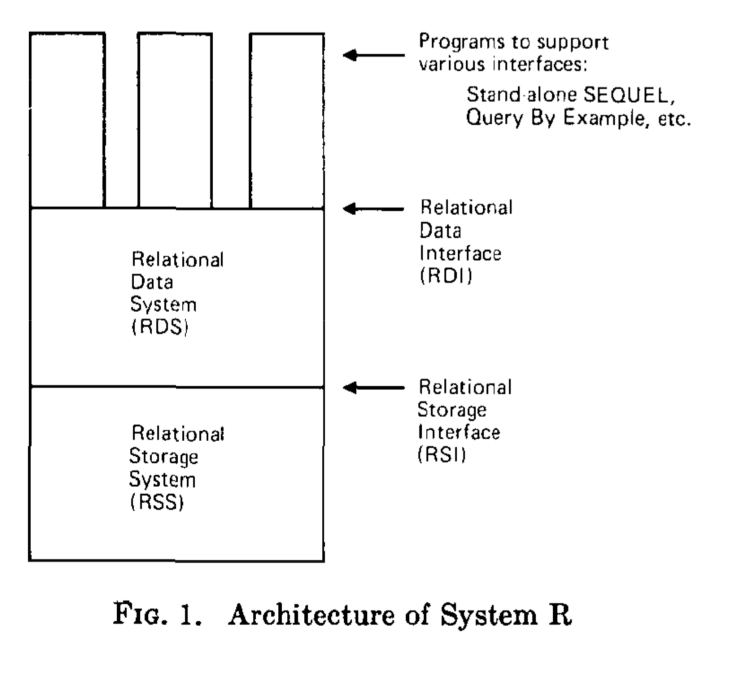
The Relational Data Interface is the external interface to the system, which can be called directly by a programming language using an early version of the SQL language as we know it today. After having received a query, the Relational Storage System performs any needed query optimization and chooses an appropriate access path to the underlying storage in the Relational Storage System.
The portions of the paper most interesting to me revolve around the storage system — the RSS. The RSS supports simple, tuple at a time access to the relational data in the database, while supporting data recovery and transaction management.
Within the RSS, data is stored in logical address spaces called segments, which are mapped to physical address space to control clustering of data. All tuples of a given relation are stored within the same segment and each segment consists of several equal sized pages. These pages are allocated and freed as data is inserted and removed from the database. Pages are copied into a main memory buffer during queries to aid with concurrency control and transaction management.
To handle segment recovery, a map between segments and pages is associated to two copies: current and backup. Any updates to a page made during a transaction are made to current and those change are saved to backup after all operations in a transaction are complete.
System-R also maintains a set of image relations. Images are a sorted view of the data allowing for the ability to efficiently scan over relations according to some sort criteria. This allows the RSS to rapidly fetch a tuple by keying on the sorted field values. The images are implemented using B-Trees.
In addition to images, System-R implements links, providing bidirectional access between parent and child relations. As new relations are defined in the database, new links are added to provide fast access between the equivalent of primary-key, foreign-key relationships. This function is important for supporting relational joins.
Transaction management is handled through the maintenance of a time ordered list of log entries, which record information about each change to data. System-R provides routines for replaying log entries or undoing log entries to handle aborted or failed transactions.
All of these facilities, or variations of them, are replicated in one way or another in modern databases such as Postgres and MySQL.
What are the contributions?
The contributions of System-R are many: relational data management, SQL support, and transaction management and recovery. The influence of the choices made by the System-R team have been felt by database practitioner’s every since.
What are future directions for this research?
Since this paper is historical, many different research directions have spun out of it. The most notable current successor of this work is the Postgres database.
What questions are you left with?
The System-R paper is a dense read with a lot of information presented in nothing more than one or two sentences. To fully appreciate the design and implementation requires careful study.
What is your take-away message from this paper?
Good design stands the test of time. It’s remarkable how many of our current design and implementations are based on initial work done by previous generations. Indeed, everything old is new again.